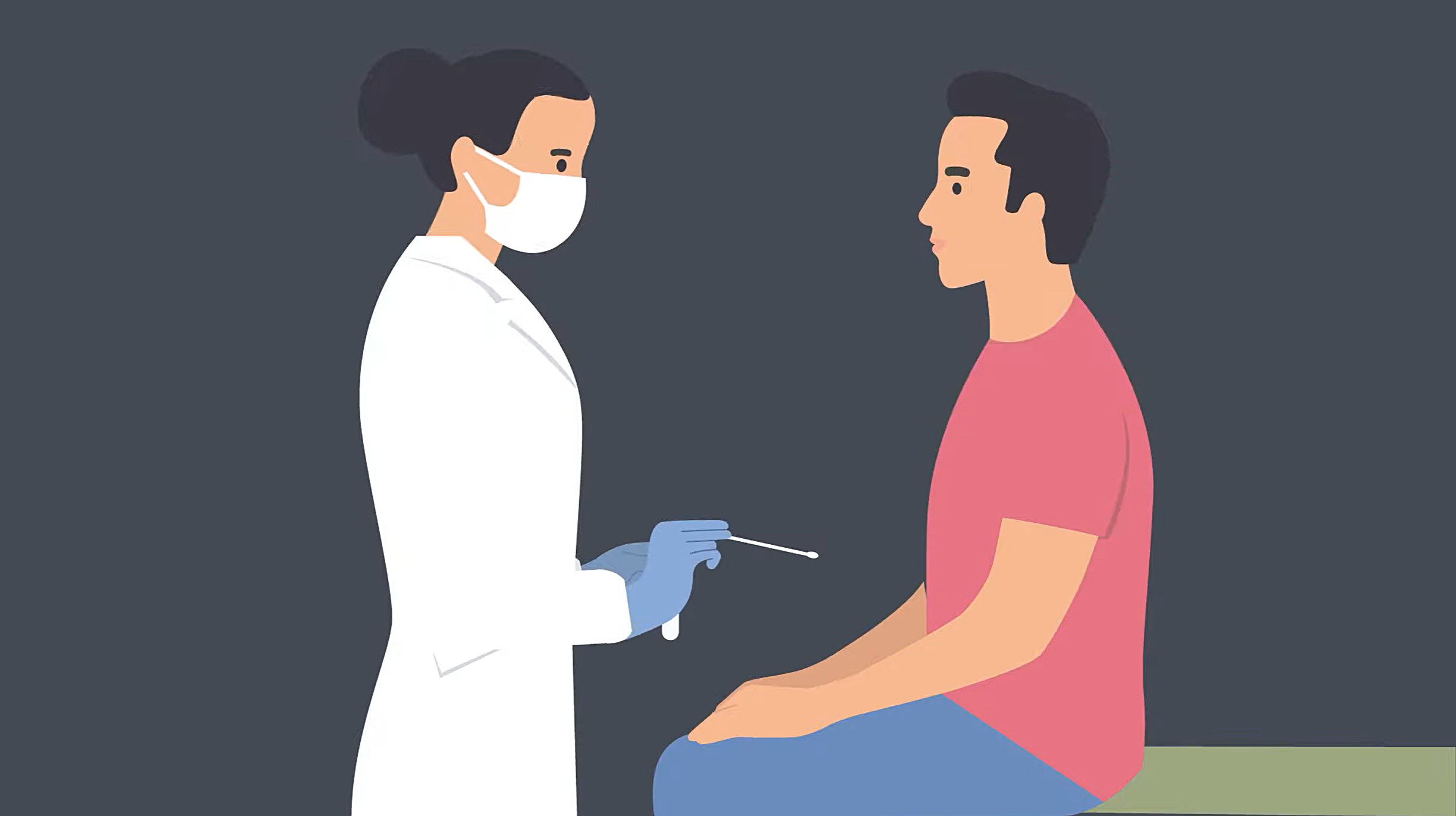

Viral tests look for a current infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, by testing specimens from your nose or mouth.
There are two main types of viral tests.

Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), including PCR tests, are more likely to detect the virus than antigen tests. NAATs tests are the “gold standard” for COVID-19 tests.
Your sample will usually be taken by a healthcare provider and transported to a laboratory for testing and may take up to 3 days to receive results. Some NAATs may be performed at the point-of-care and provide results more quickly.
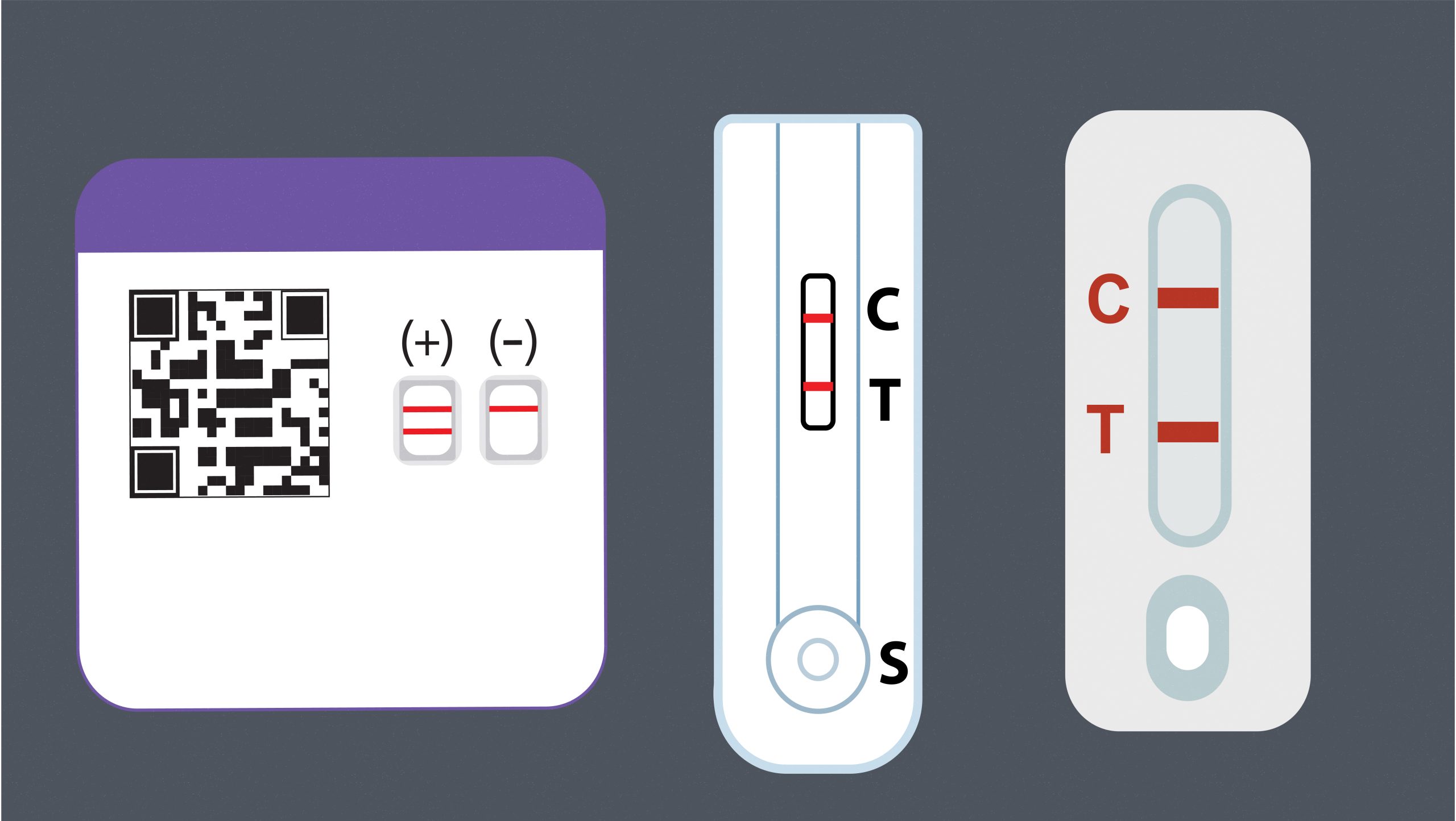
Antigen tests* are rapid tests that usually produce results in 15-30 minutes. Positive results are accurate and reliable. However, in general, antigen tests are less likely to detect the virus than NAAT tests, especially when symptoms are not present. Therefore, a single negative antigen test cannot rule out infection.
To be confident you do not have COVID-19, FDA recommends 2 negative antigen tests for individuals with symptoms or 3 antigen tests for those without symptoms, performed 48 hours apart. A single NAAT test can be used to confirm an antigen test result.
*Self-tests, or at-home tests, are antigen tests that can be taken anywhere without having to go to a specific testing site. Read self-test package inserts thoroughly and follow the instructions closely when performing the test.